
What Makes the Internet Computer Unique?
The Internet Computer is unlike any other blockchain, and that's why IC enthusiasts refer to it as a world computer. But in what way does it challenge other blockchains as well as powerful web2 tech companies? In short, what makes the Internet Computer unique?
The Internet Computer is unlike any other blockchain, and that's why IC enthusiasts refer to it as a world computer. But in what way does it challenge other blockchains as well as powerful web2 tech companies? In short, what makes the Internet Computer unique?
Let’s take a look at how the Internet Computer Protocol blockchain really shows off the power of web3!
#1 Transactions that Take Place at Web Speed
One of the things that have hindered web3 adoption is that blockchain transactions are usually much slower than interactions with traditional web2 applications. But the Internet Computer has changed all of that. With finality occurring in under two seconds, dApps on the Internet Computer can query and update at web speed. In other words, transactions take place at the speeds we have all grown accustomed to when using web2 applications.

How is this possible? Despite the jokes many of us in the community make, it’s not actually alien technology. It’s possible thanks to breakthrough tech called Chain Key Cryptography. Since the top cryptographers in the world work at the DFINITY Foundation, it’s better if I let them explain Chain Key Cryptography on their blog.
#2 The Reverse Gas Model
One of the biggest complaints people have about the Ethereum blockchain (and many others) is fluctuating gas fees. Why should you have to wait to make a transaction so you can get a better deal on the fees? And can you imagine a social media app that runs on a blockchain with gas fees? There are numerous dapps on other blockchains that require you to connect a wallet and pay a fee every time you interact with them, even when creating a new account. This isn't the way to attract web2 users to adopt decentralized apps.
The Internet Computer solves the gas fee problem with reverse gas fees.
When developers set up a canister (IC smart contract), they pre-pay for the fees by loading what is called cycles. Basically, the cost of computation cycles is baked into the smart contract so that users can interact with the dApp using a normal browser without having to connect a wallet and pay fees. This allows Internet Computer dApps to be 100% hosted on-chain (no AWS or other centralized hosting services).
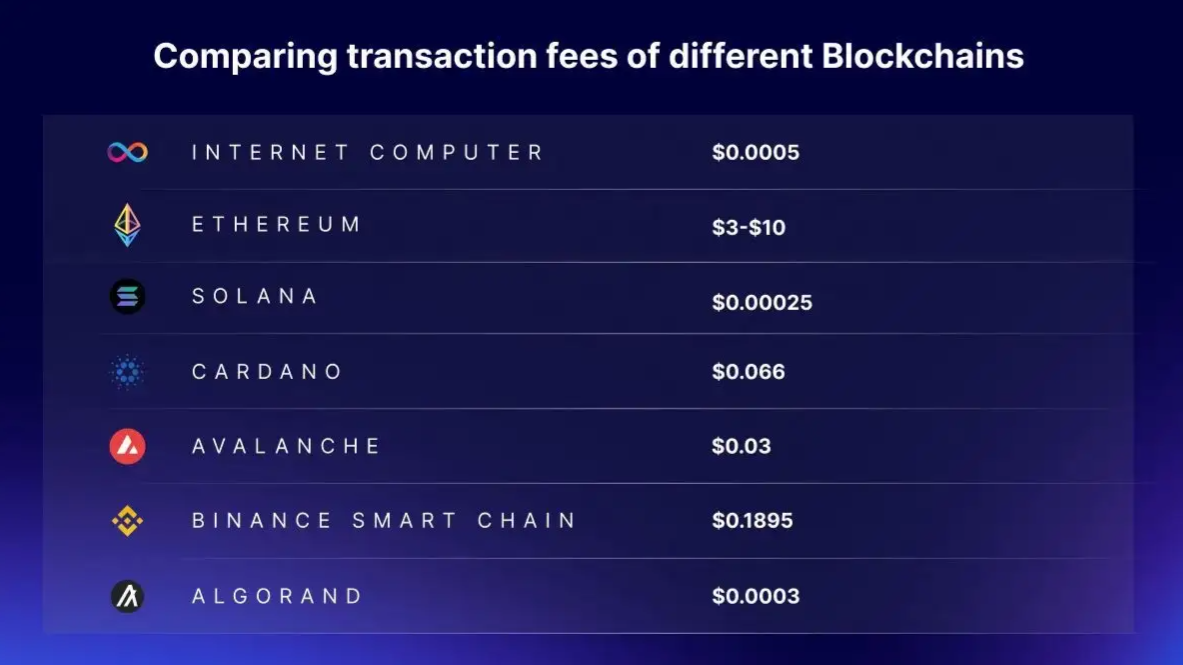
Cycles are stable and do not fluctuate in cost with the price of ICP, so developers can be confident in knowing how much the fees will cost. The development team can reload more cycles later as they run low.
NOTE: There may be occasions where a user pays a small fee (0.0001 ICP) for transfers, such as when sending tokens between wallets or purchasing an NFT.
#3 A Green Blockchain
The Internet Computer has managed to combine all of this speed and affordability while still using a minimal amount of energy. One of the main concerns about blockchain use, in general, is energy consumption. Meanwhile, a transaction on the Internet Computer uses just 1/500 of the energy of a transaction on Ethereum!
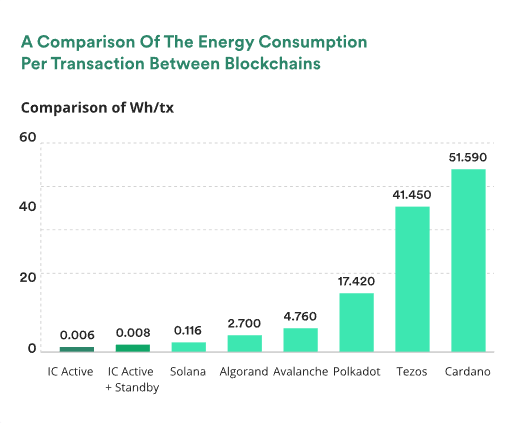
Of course, you may say that using less energy than other blockchains is easy. But the Internet Computer is also ahead of web2 tech companies when it comes to energy consumption. For example, a single Google search consumes a comparable amount of energy to four Internet Computer transactions!
The Internet Computer is already lightyears ahead of the competition when it comes to being eco-friendly, in both web2 and web3, and that competitive edge is continually being honed to ensure a sustainable future for the blockchain.
#4 Affordable On-Chain Storage
If you've ever heard an interview with Dominic Williams (Founder and Chief Scientist at the DFINITY Foundation), you've probably heard him discuss the fact that ICP projects have the ability to be built on-chain. While projects on other blockchains may make this claim, the actual websites and dApps are usually hosted on AWS or other centralized cloud hosts. Why is this the case?
If you look at the chart below, it is simply a numbers game. How could any company afford to build on the Ethereum blockchain when storing just one GB of data on the blockchain would put most companies out of business? Even on comparatively more affordable chains like Cardano or Solana, this is still way too much overhead when compared to the affordability of centralized web hosting services. No web3 startup project could afford those prices.
The astounding affordability of on-chain storage for the Internet Computer (about $5/year for one GB of data) creates an environment where on-chain storage is finally possible! And affordable on-chain storage paves the way for other web3 values, such as decentralization and censorship resistance.
#5 The SNS Will Perpetuate Autonomous dApps and Web3 Services
This is yet another essential element to building a web3 blockchain, and only the Internet Computer is already offering this type of solution. The SNS (Service Nervous System) allows crypto projects to launch a "decentralization sale" of network governance tokens. This allows a business to be run without a board of directors but rather with the network governance taking place 100% on-chain.

What Makes the Internet Computer Blockchain a World Computer?
The Internet Computer blockchain makes it affordable and feasible to host unstoppable, tamperproof code on-chain. This allows for a decentralized internet that runs everything from social networks to enterprise systems. So what makes the Internet Computer unique? It is a true world computer capable of hosting everything we interact with in a decentralized manner consistent with web3 values.

